Solutions to climate change can be divided into:
The release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere has historically been, and in many cases still is, without cost to the polluter. This is termed an 'externality', in reference to the fact the impacts of greenhouse has emissions have not correctly been factored into the decision making of those responsible. To address this, policies are required to correct this and to ensure the environmental, social and economic costs of climate change are properly considered in people's actions.
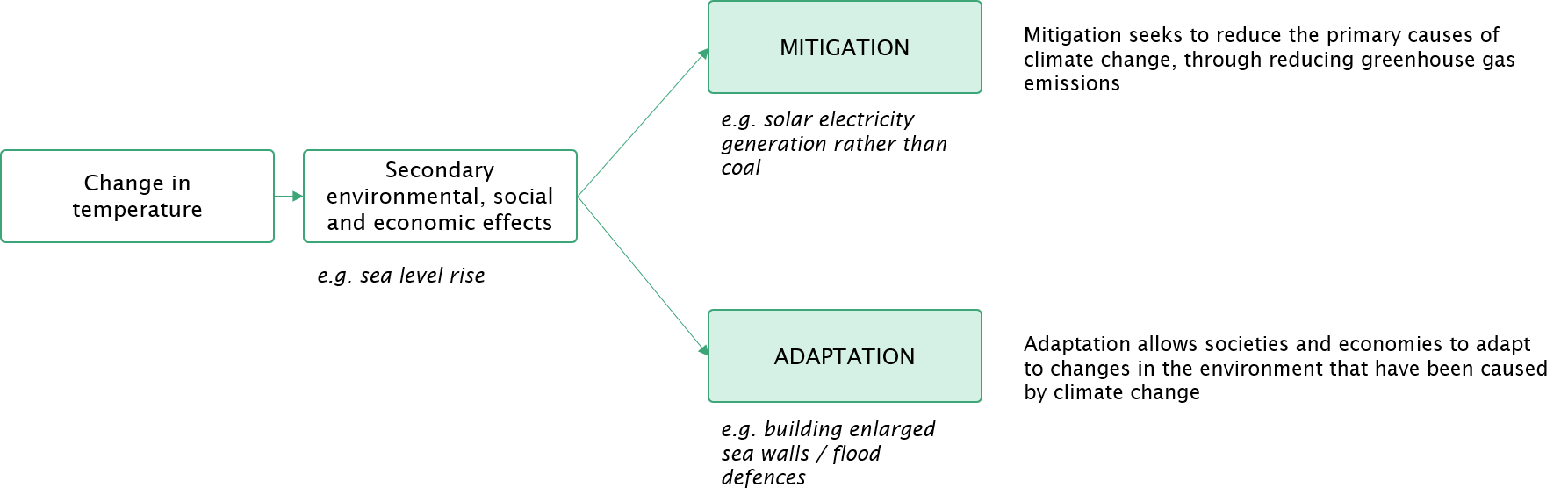
This section explores the solutions to climate change. It describes the ways in which we can mitigate any further causes of climate change to minimise the effects; as well as identifying the ways humans will be required to adapt to changes in the environment that have already occurred, or are likely to occur in the future.
The solutions to climate change can be divided into mitigation and adaptation:

The mitigation of climate change involves a reduction in those activities causing the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Accepting that human development is dependent on the status quo, a number of approaches to mitigation involve the replacement of unsustainable practices with more sustainable alternatives. This section explores the technology and the cost behind these alternatives.
Click here for more detail.
Climate change is already occurring, and is already having effects on the environment in those most sensitive places of the earth. The knock on effect on societies and economies of adverse changes to their environments is already being felt in some places. It is therefore necessary for those societies and economies to adapt to the changes in the environment that have occurred, and are likely to occur in the future. This section explores the technologies, costs, case studies and organisations involved in adaptation.
Click here for more detail.
Climate change is an example of an externality within an economic system; the true costs of damage to the environment are not correctly priced into economic decision making. There is therefore a cost to a society of implementing mitigation and adaptation measures where such measures 'internalise' this externality, over and above the cost of the status quo. Who bears this cost is a question of equity (fairness) and involves a multi-dimensional consideration across different locations, generations and stages of development.
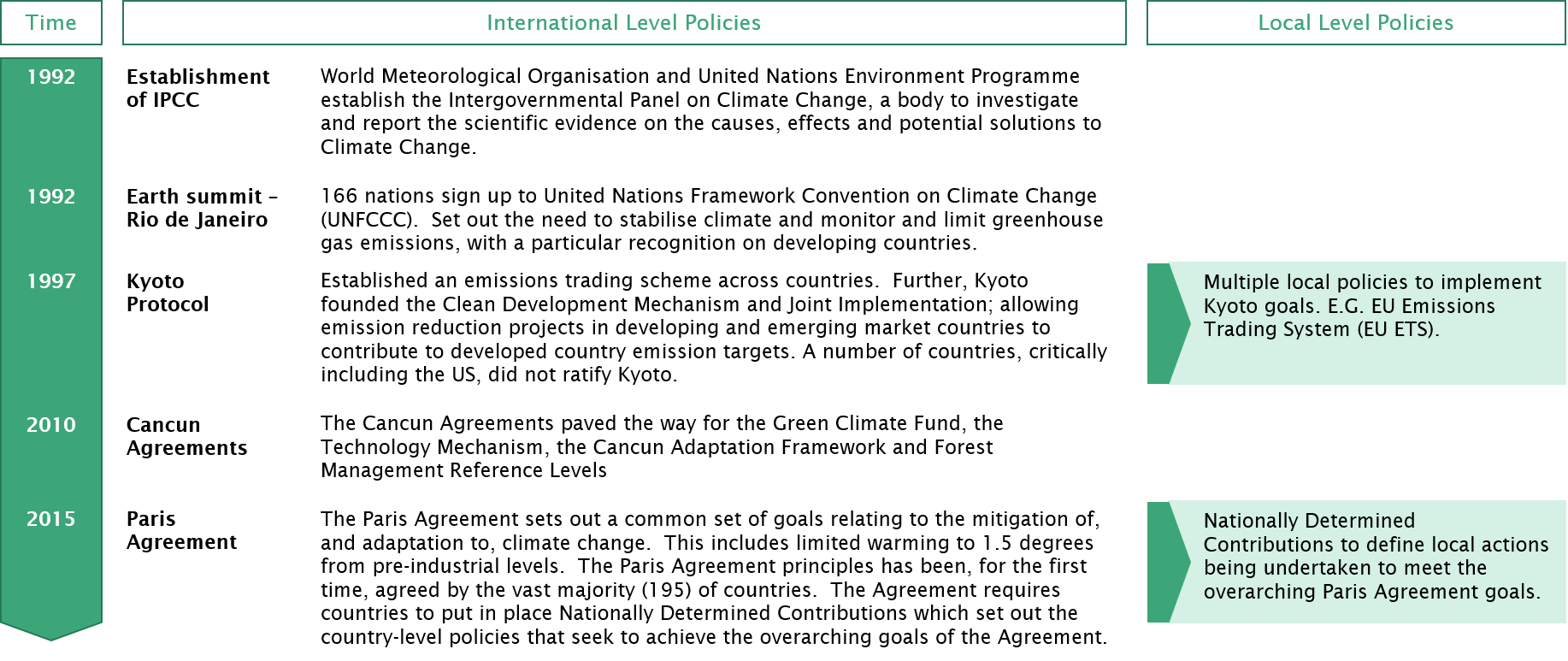
To 'internalise' this 'externality' governments across the world have sought to implement policies that promote the mitigation of, or adaptation to, the effects of climate change. The diagram below summarises a brief history of international climate change policies. Explore more detail on climate change policies in the Policy Directory